Perspective on Hot Forming Technology
A take on hot forming technology and hot formed Advanced High Strength Steels.
Hot Forming Technology has earned itself a reputation for being capital intensive, energy guzzling, slower, costly, difficult but hot forming and warm forming become inevitable for:
- Lightweighting of vehicles and aircraft for lesser emissions and fuel cost saving through their service life;
- Lightweighting while improving crash performance of cars owing to higher strength material usage for their structural members (safety cage);
- Killing the ill effects of higher springback and reducing the forming force for higher strength material;
- Getting over the poor formability and lower ductility;
- Extending the application window for other forming technologies with addition of Hot Forming Supplement e.g. Incremental Forming, Hydroforming, Roll Forming etc.
Boron-based AHSS
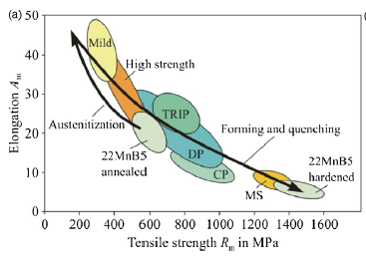
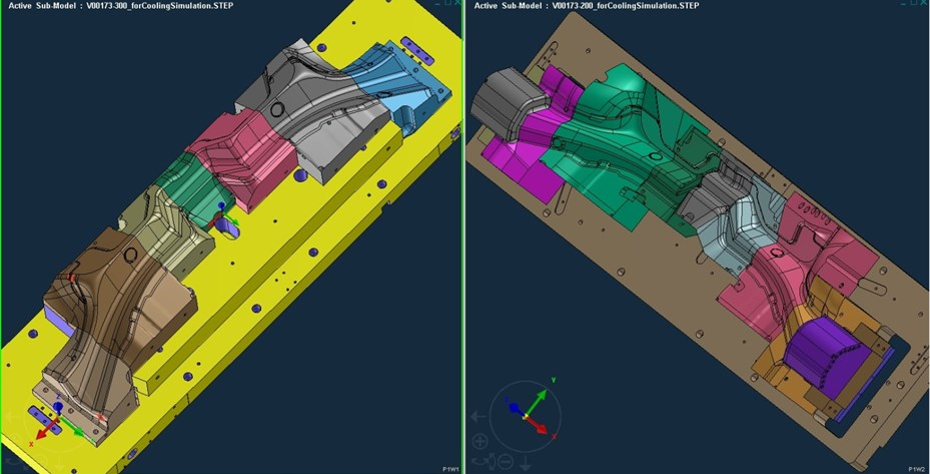
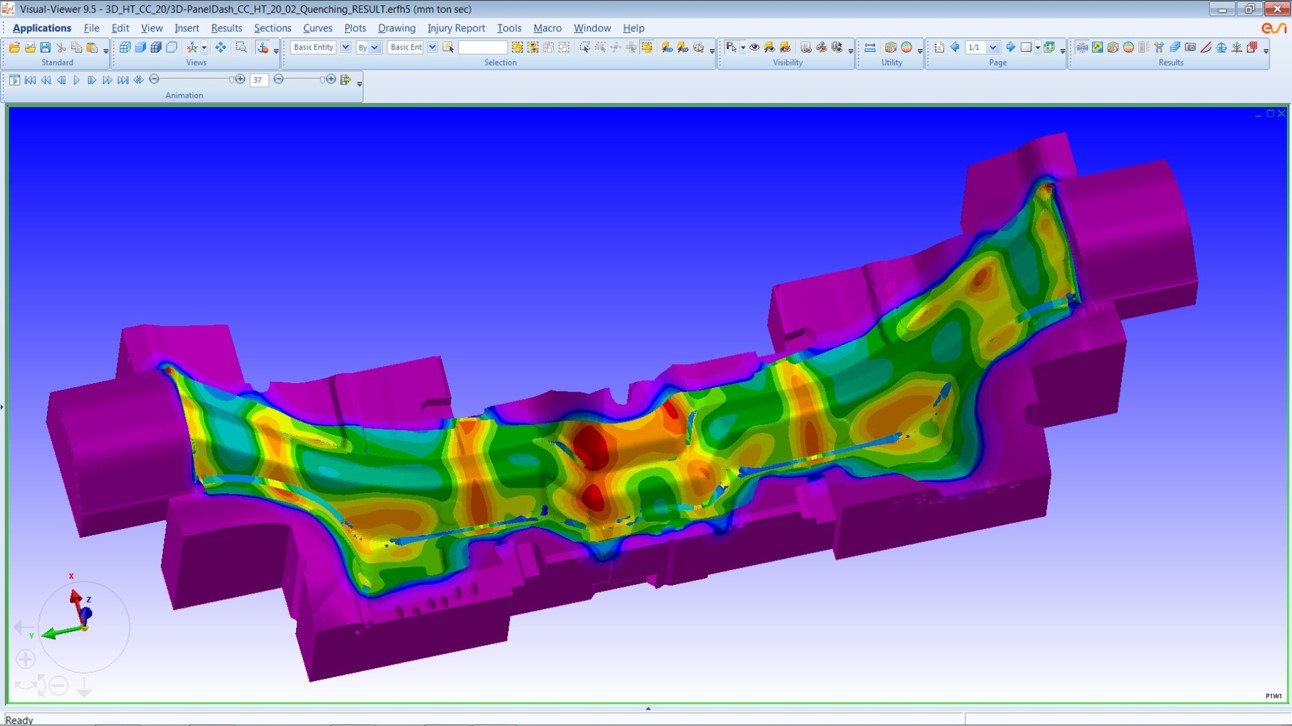
The process of hot forming of Boron-based Advanced High Strength Steels (AHSS) involves :
- The temperature is raised to Austenizing temperature of 950oC, blanks are heated in long furnaces with conveyor and material handling can only be through robots;
- While forming, the sheets are rapidly cooled through die;
- Depending upon the Cooling Curve vis-à-vis TTT (Temperature Time Transformation) diagram, the extent of precipitation of Martensite and consequently the strength acquired by part upon cooling varies;
- In addition to Forming, the dies have additional requirement of rapid heat extraction so they are segmented with separate conformal coolant channels, independent guiding and cushioning for maximizing contact area with formed sheet part profile;
- The Forming Press must be Hydraulic or Servo since it must dwell upon bottoming while pressing;
- The part becomes so hard on forming that it could only be Laser cut subsequently and no ‘restrike’ operation is possible;
- For welding, parts must be locally softened by Induction / Laser annealing;
- It is possible to tailor high or lower strength locally in a part by differential heating of blank or cooling rate upon forming apart from using Tailor Welded Blank;
- Hot Forming deserves a full software eco-system to design parts using differential properties, to design dies and to simulate forming with mechanics, elasticity, heat flow, computation fluid dynamics as well as to forecast metallurgical phase distribution.

For further insight into hot forming technology, ISFT20 would be hosting a few sessions. IMTEX FORMING 2020 is also holding a one-day training session on January 24, 2019 which would be conducted by Avinash Khare and the faculty from AP&T Sweden.





 Facebook
Facebook.png) Twitter
Twitter Linkedin
Linkedin Subscribe
Subscribe