ECONOMY REFLECTS UPBEAT MARKET SENTIMENT
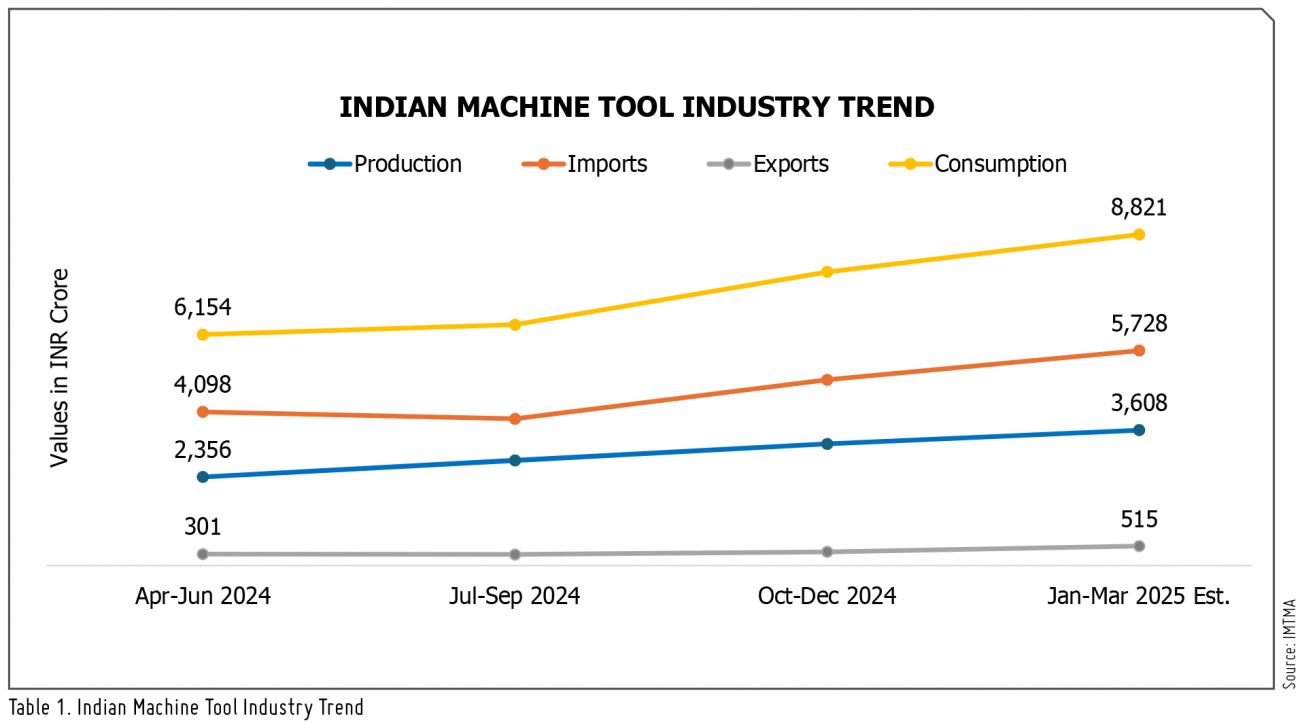
India’s economy showed steady momentum in early 2025, with strong PMI figures, easing inflation, and a supportive policy stance. The machine tool industry recorded 5% production growth and 16% higher consumption, despite a decline in exports. Rising imports from China, Japan, and Germany highlight continued domestic demand and global engagement.
In March 2025, India’s macroeconomic landscape exhibited promising signs, with manufacturing PMI (Purchasing Managers' Index) increased to an eight-month high of 58.1. Services PMI also continued to remain at a high level of 58.5.
IIP (Index of Industrial Production) growth moderated to a six-month low of 2.9 percent in February 2025 due to a fall in the growth of manufacturing and mining output.
Inflation Eases, RBI Adopts Growth-Friendly Stance
Despite this momentum, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) reduced the repo rate by 25 basis point to 6.0 percent in its monetary policy review held on April 2025. It also changed the policy stance from ‘neutral’ to ‘accommodative’ in order to support growth. Meanwhile, CPI (Consumer Price Index) inflation eased to a 67-month low of 3.3 percent in March 2025, while WPI (Wholesale Price Index) inflation moderated to 2.0 percent in March 2025 from 2.4 percent in February 2025.
Government Revenues Rise Despite Fiscal Pressures
On the fiscal front, the Government of India (GoI) witnessed a growth in gross tax revenues (GTR) by 10.9 percent during April-February FY25. However, fiscal and revenue deficits during April-February FY25 stood at 85.8 percent and 93.8 percent, respectively of their annual Revised Estimates (RE).
Trade and Investment
The banking sector witnessed a surge in gross bank credit by 12.0 percent in February 2025, marginally lower compared to 12.5 percent in January 2025, while the current account deficit narrowed to 1.1 percent of GDP in 3QFY25 from 1.8 percent in 2QFY25.
Merchandise trade deficit increased to US$ 21.5 billion in March 2025 from US$ 14.1 billion in February 2025, owing to a surge in oil and gold imports. Merchandise exports and imports turned positive at 0.7 percent and 11.4 percent, respectively, in March 2025 from a contraction of (-)10.9 percent and (-)16.3 percent, in February 2025.
FDI (Foreign Direct Investment) and FPI (Foreign Portfolio Investment) witnessed outflows amounting to US$ 1.2 billion and US$ 4.0 billion respectively in February 2025, and global crude price fell to US$ 70.7/ bbl in March 2025, its lowest level since August 2021. The IMF (International Monetary Fund) has projected global growth at 2.8 percent in 2025, with India’s FY26 growth forecasted at 6.2 percent.
Machine Tool Industry: Consumption and Production Up, Imports Surge, Exports Down
The Indian Machine Tool industry’s production in FY2024-25 is estimated to have increased by 5 percent to reach INR 14,286 crore (US$ 1.7 B). The industry’s imports in FY2024-25 saw a rise of 22 percent year-on-year, amounting to INR 18,686 crore (US$ 2.2 B). Machine tool exports during FY2024-25 from India reported a -11 percent degrowth on a low base, amounting to INR 1,472 crore (US$ 173 M) and consumption is estimated to have increased by 16 percent to reach INR 31,500 crore (US$ 3.7 B) in FY2024-25.
In FY2024-25, China (25%), Japan (19%), and Germany (12%) emerged as the top countries for imports to India, contributing to 56 percent of the total machine tools imports. Presses (17%), Vertical Machining Centers (VMCs) (12%) and Lathes (10%) were the top machinery types imported, valued at INR 7,275 crore (US$ 858 M), constituting approximately 39 percent of total machine tool imports during the period.
On the export front, Russia (20%), the UAE (13%), and Saudi Arabia (10%) emerged as the major destinations, collectively representing 43 percent of total machine tool exports in FY2024-25 and amounting to a total export value of INR 1,472 crore (US$ 173 M). Among the machinery types, Lathes (17%), Presses (14%) and VMCs (12%) stood out as the top three machinery types exported, with a combined value of INR 629 crore (US$ 74 M), accounting for roughly 43 percent of total machine tool exports during FY2024-25.
|
Machine Tool consumption is estimated to have increased by 16% to reach INR 31,500 crore (US$ 3.7 B) and Imports to India saw a rise of 22% amounting to INR 18,686 crore (US$ 2.2 B). |
Source: Data & Policy Team, IMTMA



 Facebook
Facebook.png) Twitter
Twitter Linkedin
Linkedin Subscribe
Subscribe