INTELLIGENT MANUFACTURING: Transforming Industrial Ecosystems

Here’s exploring how manufacturing leaders can leverage AI as a transformative force. The future belongs to those who recognize that Artificial intelligence (AI) is no longer just about automation. It’s about autonomy, intelligence, integration and a new more effective way of working.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is reshaping every facet of manufacturing. From design to production, supply chains to sales, and workforce management, AI is unlocking new efficiencies and enabling smarter, more agile operations. It’s also powering sustainability, helping manufacturers minimize waste and optimize energy use.
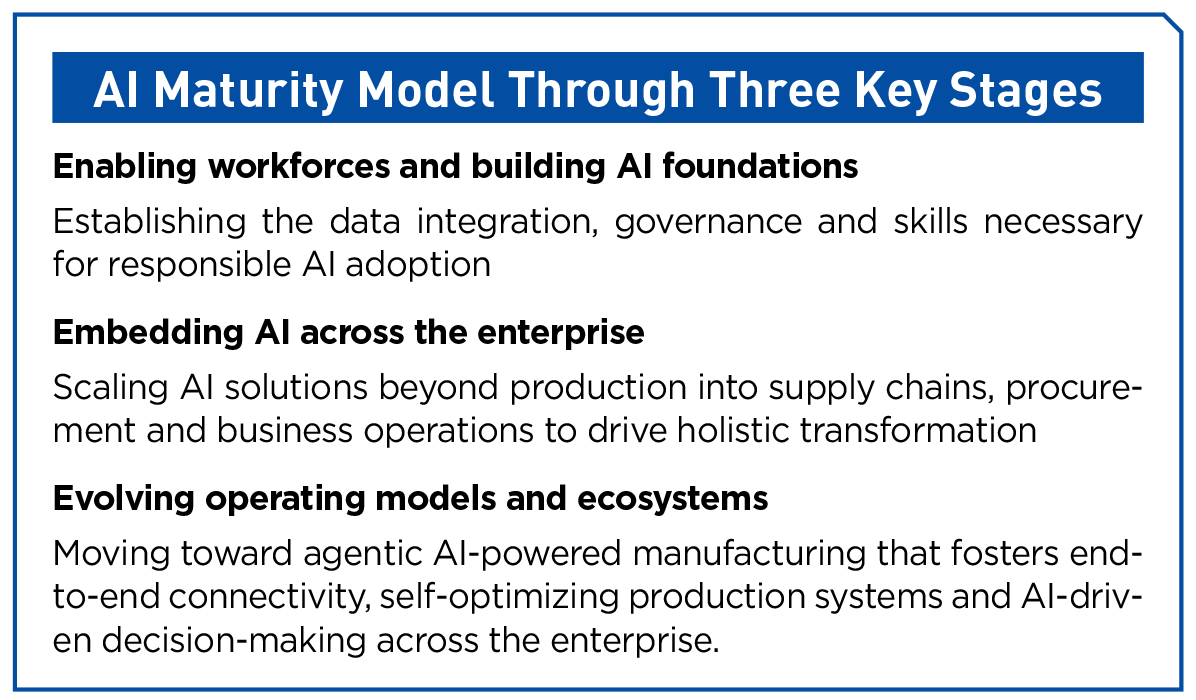
The potential is vast, but so are the challenges. AI adoption remains fragmented and functionally driven. Many manufacturers are deploying AI in silos — production floors are embracing AI-driven automation and predictive maintenance, while back-office functions remain largely unintegrated and lacking automation. This disjointed approach limits AI’s full potential, preventing the industry from achieving true enterprise-wide transformation.
The sector also presents a stark contrast in maturity levels. Smart industrials are leading the charge, embedding AI deeply into their operations. More traditional manufacturers are still experimenting with localized AI use cases, hesitant to commit to full-scale transformation. Meanwhile, agentic AI, the next frontier in intelligent tools, waits in the wings.
By enabling self-optimizing supply chains, autonomous production lines and real-time coordination across business functions, agentic AI paves the way for a truly intelligent, end-to-end manufacturing model. But to fully realize its potential, manufacturers should move beyond isolated AI implementations and embrace a connected, enterprise-wide approach.
| Many manufacturers are deploying AI in silos — production floors are embracing AI-driven automation and predictive maintenance, while back-office functions remain largely unintegrated and lacking automation. |
A Transformational Shift

This report from KPMG explores how manufacturing leaders can leverage AI as a transformative force. AI leaders in the sector recognize that embracing AI is no longer optional but a strategic necessity — 93 percent believe that organizations that fully integrate AI will gain a significant competitive edge over those that do not.
It is quickly becoming integral to operations: 20 percent of manufacturers consider AI a core component across all departments. Furthermore, 26 percent have embedded AI into their organizational culture and operations, using it to drive innovation, create new business models, and explore untapped markets.
Agile and Hybrid Organizational Models
To support AI adoption, manufacturing firms are rethinking their organizational structures. Nineteen percent have adopted an agile approach, where teams are cross-functional, adaptable and focused on specific projects or goals to ensure rapid iteration and delivery. However, 50 percent have implemented a hybrid model, blending multiple approaches such as functional and agile structures to optimize flexibility and efficiency.
Cloud, On-Premises

While 60 percent have predominantly cloud-based IT systems, AI adoption remains rooted in both cloud and on-premises infrastructure; in fact, 84 percent are leveraging on-premises AI solutions. The ability to manage and integrate data effectively is also a priority, with 52 percent implementing cross-platform data integration or intelligent data fabrics, and 74 percent making significant use of AI-powered data platforms.
Advanced AI Capabilities In Manufacturing
AI applications in industrial manufacturing are rapidly expanding. Seventy-four percent of organizations are utilizing machine learning, while 72 percent are leveraging predictive analytics. Process automation is also a key focus, with 67 percent integrating AI with RPA. Notably, 67 percent are using agentic AI, with an additional 20 percent planning to expand its use. Confidence in AI’s decision-making capabilities is high: 91 percent are comfortable allowing AI to make end-to-end autonomous decisions for specific processes.
Impact On Key Business Functions
AI adoption is having the greatest impact on R&D and IT functions, according to 77 percent of industry leaders. However, its influence extends across the value chain, with 70 percent citing significant operational improvements as AI becomes embedded into core business functions.
Investment Trends And Budget Prioritization
Investment in AI is accelerating, with 36 percent of manufacturers allocating over 10 percent of their total IT budget to AI. Looking ahead, 77 percent plan to increase AI investments over the next year, with 71 percent expecting growth of more than 10 percent. The primary objectives of these investments are clear: 72 percent aim to enhance efficiency, with 52 percent focused on process automation and 77 percent using AI to drive business growth.
Measuring AI’s Business Impact
The benefits of AI adoption are already materializing. Ninety-six percent of organizations have reported operational and efficiency gains, while 45 percent have experienced measurable financial improvements. Return on investment (ROI) is a key metric, with 62 percent achieving an ROI greater than 10 percent and 31 percent expecting AI investments to yield a return of over 30 percent in the next 12 months.
AI Upskilling and Workforce Readiness
Workforce preparedness is a critical enabler of AI adoption. Recognizing this, 80 percent of organizations have invested in AI knowledge and skills training, while 72 percent have focused on building a comprehensive business AI strategy. Encouragingly, 89 percent believe employees are quickly adapting to AI tools and technologies, supporting widespread adoption across the workforce. Encouraging cross-functional collaboration between AI specialists, engineers and frontline workers helps ensure that AI adoption uplifts workforces.
Balancing AI with Sustainability Goals

While AI adoption is accelerating, manufacturers are also conscious of its broader implications. Seventy-eight percent believe meeting sustainability targets is more important than AI, highlighting the sector’s commitment to responsible innovation. Additionally, 85 percent have strategies in place to mitigate AI’s increasing energy demands, ensuring AI adoption aligns with long-term sustainability goals.
Create a Sustainable Technology
Maximizing value from AI depends on integrated, scalable and secure data infrastructure. Organizations should build a connected data ecosystem that integrates research and development (R&D), production and field service data. Cloud-based AI platforms, intelligent edge computing and cross-platform data fabrics enable real-time AI-driven insights and interoperability across legacy systems and new digital technologies.
Transformative Role of Agentic Autonomous Agents
Agentic autonomous AI — AI-driven systems capable of independent reasoning, decision-making and goal-oriented execution — can fundamentally reshape industrial manufacturing. These AI agents can proactively manage complex processes, adapt to changing conditions and collaborate with humans and other systems to drive efficiency, innovation and resilience.
Agentic AI can introduce self-directed, goal-oriented decision-making across various manufacturing processes. Key areas of future transformation include:
| Investment in AI is accelerating, with 36% of manufacturers allocating over 10% of their total IT budget to AI. |
Autonomous Production Lines
AI agents can optimize production schedules in real time based on demand, resource availability and machine performance. They can detect and correct defects proactively, reducing waste and enhancing quality control. Self-optimizing robotic systems can collaborate with human workers to enhance efficiency while maintaining flexibility. It can track process parameters and adjust other machine parameters to maximize yield to optimize costs and drive consistency.
Self-Optimizing Supply Chains
AI agents can drive intelligent commodity forecasting by tracking multiple market indices in real time and adjust procurement strategies dynamically to optimize costs and balance risks. AI agents can also optimize the share of business (SOB) processes by identifying cost-saving opportunities, flagging anomalies and streamlining approvals — driving greater efficiency, compliance and value across the procurement value chain.
Asset Management
AI-driven agents can predict and prevent equipment failures by continuously analyzing sensor data. Autonomous systems can schedule and execute maintenance tasks without human intervention, minimizing downtime. Digital twins, powered by agentic AI, can simulate wear and tear, testing different maintenance strategies to extend machine lifespan. AI agents also help in understanding failure patterns of equipment, identify critical spares, redesign spare part policies and release auto purchase orders based on minimum inventory thereby enabling minimum downtime.
Human-AI Collaboration in Decision-Making
AI agents can assist production managers by analyzing complex scenarios and proposing optimized strategies. Intelligent copilots can provide real-time recommendations to factory workers on the shop floor, improving decision-making speed and accuracy. AI-driven training simulations can provide personalized learning experiences, accelerating workforce upskilling.
Circular Economy and Sustainable Manufacturing AI agents can help optimize material usage and recycling efforts by identifying waste reduction opportunities across the production cycle. Autonomous systems can track carbon emissions in real time, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations. AI-driven energy management systems can dynamically adjust power consumption to help minimize costs and environmental impact.
Data Problem in Manufacturing
Manufacturing generates vast amounts of data — from R&D labs to the shop floor to field service operations. However, this data is often fragmented, siloed and disconnected, hiding insights and limiting its potential value. Manufacturers can unlock real value by integrating R&D, production and field service data into a closed-loop system. Without this integration, manufacturers struggle to turn data into actionable insights, missing opportunities for efficiency, innovation and cost reduction.
Manufacturing data is not just siloed — it is also highly heterogeneous. Products vary widely in complexity, requiring different data structures and analytics approaches. Ownership of data is fragmented across multiple stakeholders — including manufacturers, customers, distributors, dealers and third-party service providers.
Data formats and standards vary across different production lines, making integration a technical challenge. Without a unified data strategy, manufacturers struggle to extract meaningful insights. They remain reactive rather than predictive, limiting their ability to optimize performance, enhance quality and accelerate innovation.
| Agentic autonomous AI — AI-driven systems capable of independent reasoning, decision- making and goal-oriented execution — can fundamentally reshape industrial manufacturing. |
Addressing the Challenge
To help maximize AI’s potential, manufacturers should move from disconnected data silos to a fully integrated, AI-
powered ecosystem. By creating a closed-loop data framework that connects R&D, production and field service, manufacturers can continuously optimize product design based on real-world performance, enable predictive maintenance and reduce unplanned downtime and improve supply chain efficiency by aligning production with demand signals from field data.
AI-driven, cross-functional data integration is the key to transforming manufacturing from a reactive industry to a proactive, intelligent ecosystem.
| Leaders need to think through how processes will change post AI implementations and how humans and AI should work together in a new way. |
In Conclusion
AI adoption in manufacturing is not just about efficiency — it is about long-term growth and transformation. This structured approach ensures AI investments align with business objectives, paving the way for sustained competitive advantage.
Manufacturers should develop a blueprint for implementing AI across the enterprise with a focus on AI applications that have a high business impact and provide operational benefits, such as predictive maintenance, defect detection production optimization and AI-driven supply chain forecasting.
AI should augment human expertise, not replace it. Leaders need to think through how processes will change post AI implementations and how humans and AI should work together in a new way. Manufacturers should reskill employees, integrate AI into factory operations and decision-making processes, and create a culture where AI enhances efficiency, safety and innovation.
Source: KPMG International Ltd



 Facebook
Facebook.png) Twitter
Twitter Linkedin
Linkedin Subscribe
Subscribe